Progressive Lenses: Navigating Common Problems and Finding Effective Solutions
Progressive lenses, also known as no-line bifocals, represent a significant advancement in vision correction. They offer a seamless transition between different viewing distances, eliminating the need for multiple pairs of glasses. This innovation allows wearers to see clearly at near, intermediate, and far distances with a single lens. However, the journey with progressive lenses isn’t always smooth sailing. Many users encounter challenges in adapting to these sophisticated lenses. This article delves into the most common problems associated with progressive lenses and offers practical solutions to ensure a more comfortable and successful experience.
Understanding Progressive Lenses
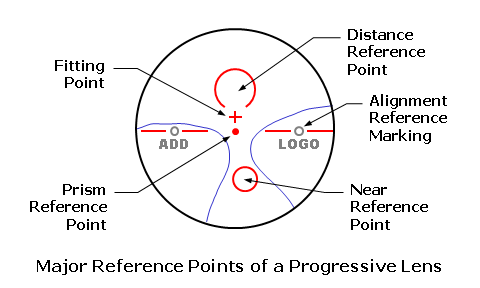
Before addressing the problems, it’s crucial to understand how progressive lenses work. Unlike traditional bifocals or trifocals, which have distinct lines separating the different focal points, progressive lenses have a gradual power change across the lens. The top portion of the lens corrects for distance vision, the middle section for intermediate vision (e.g., computer use), and the bottom portion for near vision (e.g., reading). This design provides a more natural and aesthetically pleasing visual experience.
Common Problems with Progressive Lenses
Despite their benefits, progressive lenses can present several initial challenges. These problems often stem from the wearer’s adaptation period, where the brain and eyes learn to utilize the different zones of the lens effectively. Here are some of the most frequently reported issues:
- Adaptation Difficulty: This is perhaps the most common complaint. The brain needs time to adjust to the varying powers within the lens. This adaptation period can range from a few days to several weeks. During this time, wearers might experience dizziness, headaches, and eye strain.
- Peripheral Distortion: The edges of progressive lenses often have areas of distortion. This can make the periphery of the vision appear blurry or wavy. This is a natural consequence of the lens design, but it can be particularly noticeable when walking or navigating new environments.
- Difficulty with Intermediate Vision: While designed to correct intermediate vision, some users find this zone less effective than expected. This can lead to eye strain when using computers or performing other tasks at arm’s length.
- Swimming or Swaying Sensation: Some wearers report a sensation of swimming or swaying, especially when moving their head or eyes quickly. This is related to the peripheral distortion and the brain’s adjustment to the lens.
- Reading Problems: While the bottom portion of the lens is for near vision, some individuals find it challenging to read comfortably. This can be due to the small reading area or the need to tilt the head to find the optimal reading zone.
- Eye Strain and Headaches: The constant effort required to adjust to the different zones of the lens can lead to eye strain and headaches, especially during the initial adaptation period.
Solutions and Strategies for Adapting to Progressive Lenses
Fortunately, most of these problems are temporary and can be managed with patience and the right strategies. Here are some effective solutions to help you adapt to your progressive lenses:
- Give it Time: The most crucial factor is patience. Allow your eyes and brain time to adjust to the new lenses. Don’t give up too quickly. The adaptation period is often the most challenging, but it usually improves over time.
- Wear Your Lenses Consistently: The more you wear your progressive lenses, the faster your eyes will adapt. Avoid switching back and forth between your old glasses and your new progressive lenses, as this can hinder the adaptation process.
- Practice Head Movements: Instead of moving your eyes to look at different distances, learn to move your head. Look up to see far away, look down to read, and look straight ahead for intermediate distances. This will help you use the different zones of the lens correctly.
- Adjusting Your Viewing Angle: When reading or working at a computer, adjust the position of your head and the object you are viewing. Experiment with different angles to find the most comfortable and effective viewing position.
- Consult Your Optometrist: If you are experiencing persistent problems, consult your optometrist. They can assess your lenses, ensure they are properly fitted, and offer advice tailored to your specific needs. They may also recommend exercises to help with adaptation.
- Consider Lens Design: Modern progressive lenses come in various designs. If you are struggling with adaptation, your optometrist may recommend a different lens design that is better suited to your visual needs and lifestyle.
- Proper Lighting: Ensure you have adequate lighting, especially when reading or working at a computer. Poor lighting can exacerbate eye strain and make it more difficult to adapt to your progressive lenses.
- Computer Use Tips: When working on a computer, position the screen at an appropriate distance and angle. Consider using a computer with a larger screen to reduce the need to strain your eyes.
- Driving Considerations: Be extra cautious when driving, especially during the initial adaptation period. Take your time to adjust to the lens and be aware of the peripheral distortion.
- Lens Cleaning and Maintenance: Keep your lenses clean to ensure clear vision. Regularly clean your lenses with a microfiber cloth and lens cleaner.
Specific Troubleshooting for Common Issues
Addressing Dizziness and Headaches
If you experience dizziness or headaches, it’s crucial to ensure your prescription is accurate. Schedule a follow-up appointment with your eye care professional. They can check the lens fit and make sure the progressive lenses are aligned correctly with your pupils. During the adaptation period, take frequent breaks, especially when performing visually intensive tasks. Stay hydrated and get enough sleep, as these factors can impact the severity of headaches.
Managing Peripheral Distortion
Peripheral distortion is a common side effect of progressive lenses. To minimize the impact, focus on moving your head rather than your eyes when looking at different distances. Be aware of your surroundings, especially when walking on uneven surfaces. Consider a lens design with a wider intermediate zone for improved peripheral vision. [See also: Tips for Choosing the Right Progressive Lenses]
Improving Reading Comfort
If you’re struggling with reading, adjust the position of your reading material. Tilting the book or magazine slightly towards you can help you find the optimal reading zone. Make sure your reading distance is appropriate. Consider using a slightly larger font size. Your eye doctor can also measure the reading area of your progressive lenses to ensure it’s adequate for your needs.
When to Seek Professional Help
While most adaptation issues resolve within a few weeks, some problems may persist. It’s important to know when to seek professional help. Schedule an appointment with your optometrist if you experience any of the following:
- Persistent dizziness or headaches after several weeks of wear.
- Unclear vision at any distance, even after adjusting your head and eye movements.
- Significant eye strain or fatigue.
- Difficulty with everyday tasks, such as driving or reading.
- Any other concerns about your vision or the performance of your progressive lenses.
The Benefits of Progressive Lenses
Despite the potential challenges, progressive lenses offer significant benefits. They eliminate the need for multiple pairs of glasses, providing a seamless visual experience. They are aesthetically pleasing, as they do not have the visible lines of bifocals or trifocals. They offer a more natural vision correction, allowing you to see clearly at all distances. With patience, proper adaptation techniques, and the guidance of an eye care professional, you can fully enjoy the benefits of progressive lenses.
Conclusion
Adapting to progressive lenses can be a process, but the rewards of clear and comfortable vision are well worth the effort. By understanding the common problems, implementing the recommended solutions, and seeking professional help when needed, you can ensure a positive and successful experience with your progressive lenses. Remember to be patient, persistent, and proactive in your approach to adapting to your new lenses. The journey to clear vision is often a collaborative one, between you and your eye care professional, and with the right guidance, you can achieve optimal visual clarity and comfort.
[See also: The Science Behind Progressive Lenses and Vision Correction]

