Navigating the World of Fillers: How to Choose the Right Filler to Minimize Migration
The quest for a more youthful appearance has led millions to explore the world of cosmetic injectables. Among these, dermal fillers have emerged as a popular choice, offering a non-surgical path to smoother skin, enhanced volume, and a refreshed look. However, the landscape of fillers is complex, with various types available, each boasting unique characteristics and potential benefits. One of the most crucial considerations when choosing a filler is the potential for migration – the movement of the filler from its initial injection site. This article delves into the intricacies of filler selection and provides a comprehensive guide on how to choose the right filler to minimize migration, ensuring optimal results and minimizing potential complications.
Understanding Dermal Fillers and Their Appeal
Dermal fillers are injectable substances designed to restore volume, smooth wrinkles, and enhance facial contours. They work by either directly adding volume or stimulating the body’s natural collagen production. Fillers are particularly effective in addressing age-related changes, such as volume loss in the cheeks, nasolabial folds, and lips. The appeal of fillers lies in their minimally invasive nature, relatively quick procedure time, and immediate results. Patients often appreciate the ability to achieve a more youthful appearance without undergoing surgery.
However, not all fillers are created equal. Different types of fillers utilize varying substances, each with its own set of properties, longevity, and potential risks. Understanding these differences is crucial for making an informed decision and achieving the desired aesthetic outcome.
Types of Dermal Fillers: A Comparative Overview
The market offers a diverse range of dermal fillers, each formulated with different materials. The most common types include:
- Hyaluronic Acid (HA) Fillers: These are the most popular type of fillers. HA is a naturally occurring substance in the body that attracts and retains water, providing hydration and volume. HA fillers are known for their versatility, reversibility (through the injection of hyaluronidase, an enzyme that dissolves HA), and relatively low risk of allergic reactions. Different HA fillers have varying densities and cross-linking, influencing their suitability for different areas and longevity.
- Calcium Hydroxylapatite (CaHA) Fillers: CaHA fillers are composed of microspheres suspended in a gel carrier. They stimulate collagen production, providing both immediate volume and long-term skin rejuvenation. CaHA fillers are often used for deeper wrinkles and volume restoration.
- Poly-L-Lactic Acid (PLLA) Fillers: PLLA is a biocompatible synthetic substance that stimulates the body’s own collagen production. It is a biostimulator, gradually increasing volume over time. PLLA fillers are often used to address volume loss in the face and improve skin texture.
- Polymethylmethacrylate (PMMA) Fillers: PMMA fillers consist of tiny PMMA microspheres suspended in a collagen-based gel. These are permanent fillers and are generally not reversible. PMMA fillers are used for more significant volume restoration and are often considered for specific areas of the face.
The selection of the appropriate filler depends on various factors, including the treatment area, the desired outcome, the patient’s skin type, and the injector’s expertise. The longevity of each filler type also varies, ranging from a few months to several years.
The Significance of Filler Migration
Filler migration refers to the movement of the injected filler from its original placement to an adjacent area. This can lead to undesirable aesthetic outcomes, such as lumps, bumps, asymmetry, and an unnatural appearance. Migration can occur with any type of filler, but the likelihood and extent vary depending on several factors.
Understanding the factors contributing to migration is essential for making informed decisions and minimizing the risk. The following sections will provide insights into these factors and strategies on how to choose the right filler to minimize migration.
Factors Influencing Filler Migration
Several factors can contribute to filler migration. These include:
- Filler Type and Properties: The viscosity, density, and cohesivity of the filler play a significant role. Fillers with lower viscosity and cohesivity are more prone to migration.
- Injection Technique: The skill and experience of the injector are paramount. Improper injection techniques, such as injecting the filler too superficially or using an excessive amount, can increase the risk of migration.
- Treatment Area: Areas with high mobility, such as the lips, are more susceptible to migration. The anatomy of the treated area, including the presence of muscles and blood vessels, also influences the risk.
- Patient Factors: Individual factors, such as skin type, age, lifestyle (e.g., smoking), and underlying medical conditions, can impact filler migration.
- Post-Treatment Care: Following the post-treatment instructions provided by the injector is crucial. Excessive pressure, massage, or strenuous activities can contribute to migration.
By understanding these factors, both patients and injectors can make informed decisions to minimize the risk of migration and achieve optimal results.
How to Choose the Right Filler to Minimize Migration: A Detailed Guide
Choosing the right filler is a critical step in minimizing the risk of migration. The following guidelines provide a comprehensive approach to selecting the most appropriate filler:
1. Consultation and Assessment
A thorough consultation with a qualified and experienced injector is the first and most crucial step. During the consultation, the injector should:
- Assess the Patient’s Needs and Goals: Understand the patient’s aesthetic goals, concerns, and expectations.
- Evaluate the Treatment Area: Examine the specific area to be treated, considering its anatomy, skin quality, and the presence of wrinkles or volume loss.
- Discuss Filler Options: Explain the different types of fillers available, their properties, benefits, and potential risks, including the risk of filler migration.
- Review the Patient’s Medical History: Identify any relevant medical conditions, allergies, or medications that may influence the choice of filler or the risk of complications.
2. Selecting the Right Filler Type
The choice of filler should be based on the specific needs of the patient and the characteristics of the treatment area. The following considerations are essential:
- Treatment Area: Different fillers are best suited for different areas of the face. For example, thinner fillers are often preferred for delicate areas like the under-eye region, while denser fillers may be used for cheek augmentation.
- Desired Outcome: The desired outcome, such as volume restoration, wrinkle reduction, or lip enhancement, will influence the choice of filler.
- Filler Properties: The viscosity, density, and cohesivity of the filler are crucial. For areas with high mobility, a more cohesive filler may be preferred to minimize migration.
- Longevity: The expected duration of the filler’s effect should be considered. Patients may prefer longer-lasting fillers in certain areas, while others may opt for temporary fillers.
3. The Importance of Injector Expertise
The skill and experience of the injector are paramount in minimizing the risk of migration. Patients should choose an injector who is:
- Board-Certified and Experienced: Look for a board-certified dermatologist, plastic surgeon, or other qualified medical professional with extensive experience in administering dermal fillers.
- Knowledgeable and Skilled: The injector should have a thorough understanding of facial anatomy, filler properties, and injection techniques.
- Uses Proper Injection Techniques: The injector should employ appropriate injection techniques, such as injecting the filler at the correct depth, using the appropriate amount, and avoiding excessive pressure.
- Provides Detailed Post-Treatment Instructions: The injector should provide comprehensive post-treatment instructions to minimize the risk of complications, including migration.
4. Post-Treatment Care and Maintenance
Following the post-treatment instructions provided by the injector is crucial for minimizing the risk of migration and achieving optimal results. These instructions may include:
- Avoiding Excessive Pressure or Massage: Avoid applying excessive pressure or massaging the treated area, as this can contribute to migration.
- Avoiding Strenuous Activities: Refrain from strenuous activities or exercises that may increase blood flow to the treated area.
- Avoiding Heat Exposure: Avoid excessive sun exposure, saunas, and hot tubs, as heat can affect the filler.
- Following Up with the Injector: Schedule follow-up appointments with the injector to monitor the results and address any concerns.
Addressing Filler Migration: Treatment Options
If filler migration does occur, various treatment options are available, depending on the type of filler and the extent of migration:
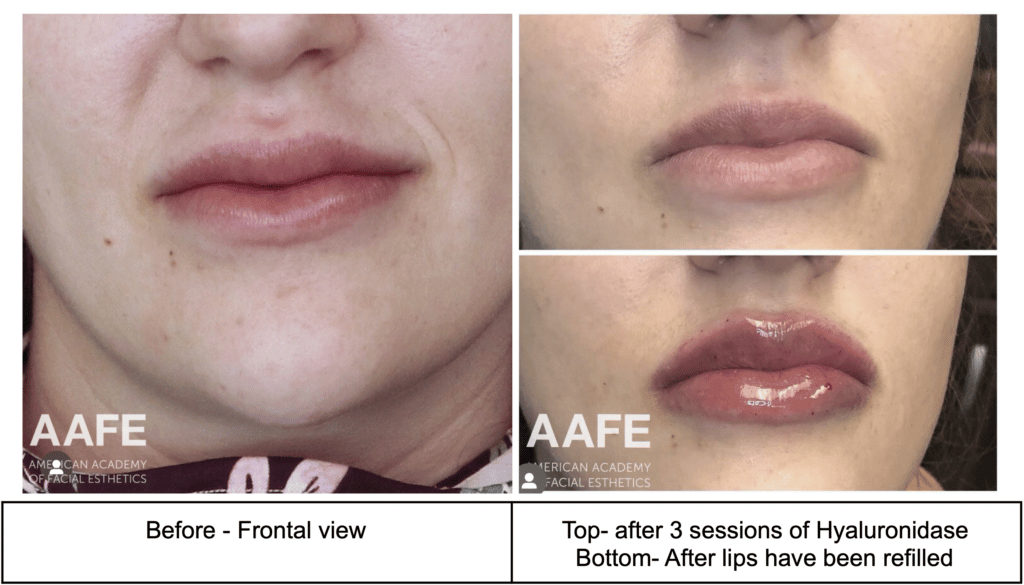
- Hyaluronic Acid Fillers: Hyaluronic acid fillers can be dissolved with hyaluronidase, an enzyme that breaks down the filler.
- Other Fillers: For other types of fillers, treatments may include:
- Massage: In some cases, gentle massage may help to reposition the filler.
- Surgical Removal: In rare cases, surgical removal may be necessary.
It is essential to consult with a qualified medical professional to determine the most appropriate treatment option.
Conclusion: Achieving Safe and Effective Results
Choosing the right filler and minimizing the risk of migration requires careful consideration and a collaborative approach between the patient and the injector. By understanding the different types of fillers, the factors influencing migration, and the importance of injector expertise and post-treatment care, patients can make informed decisions and achieve safe and effective results. The key is to prioritize safety, seek the guidance of a qualified medical professional, and follow the recommended guidelines to ensure a positive and satisfying aesthetic outcome. Ultimately, taking the time to understand how to choose the right filler to minimize migration is an investment in both beauty and peace of mind. [See also: Dermal Filler Risks and Complications]
The information provided in this article is intended for general knowledge and informational purposes only, and does not constitute medical advice. It is essential to consult with a qualified medical professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.

