Male Reproductive System: A Complete Guide
The male reproductive system, a complex and intricate network of organs and structures, is responsible for the production, storage, and delivery of sperm. This comprehensive guide delves into the anatomy, function, and potential health issues associated with the male reproductive system, providing a thorough understanding of its vital role in human reproduction.
Understanding the male reproductive system is crucial for men’s health and well-being. This guide provides a detailed look at each component, explaining its role and how it contributes to overall reproductive function. The information presented here is based on current scientific understanding and aims to be accessible and informative for a broad audience.
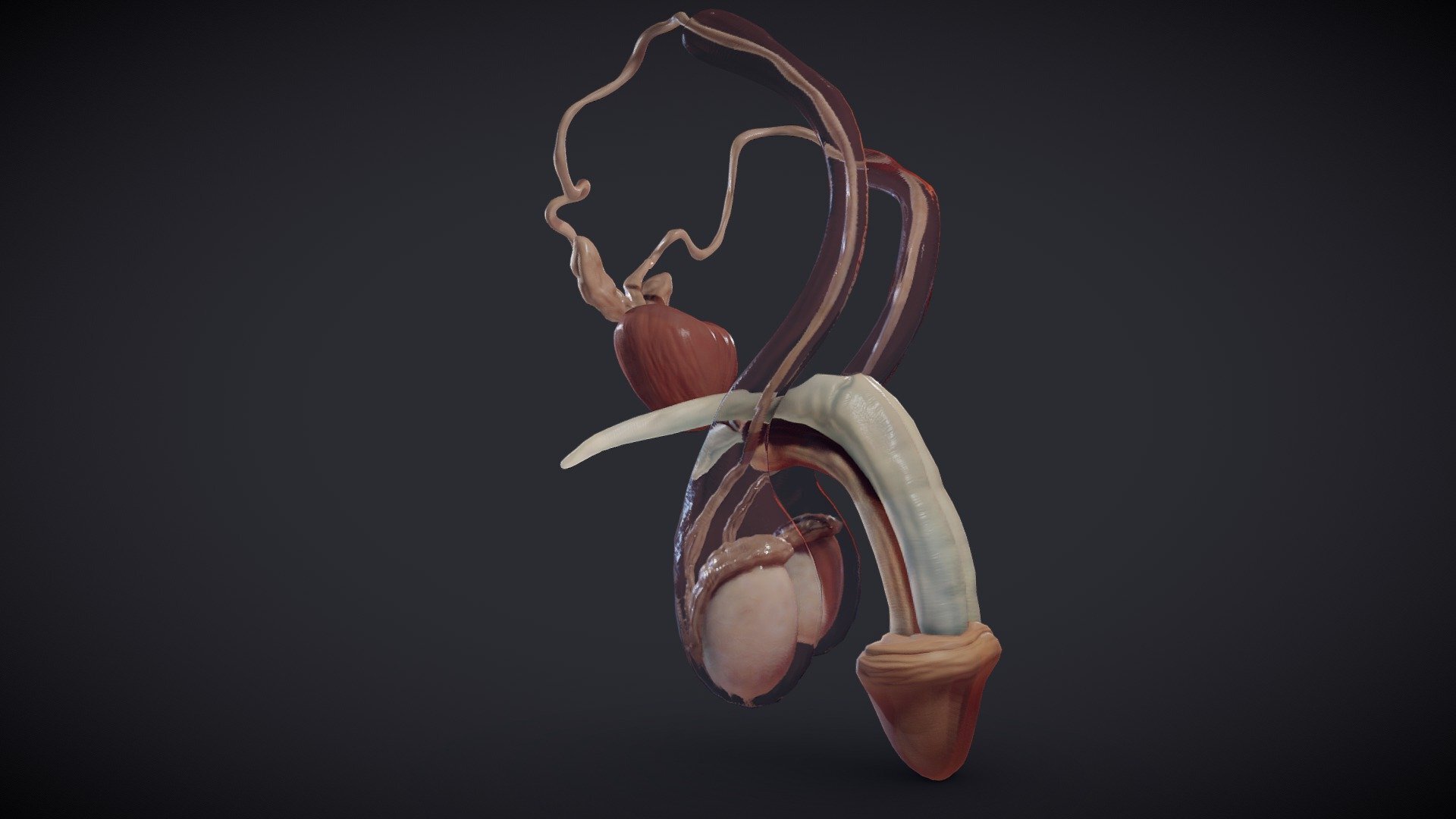
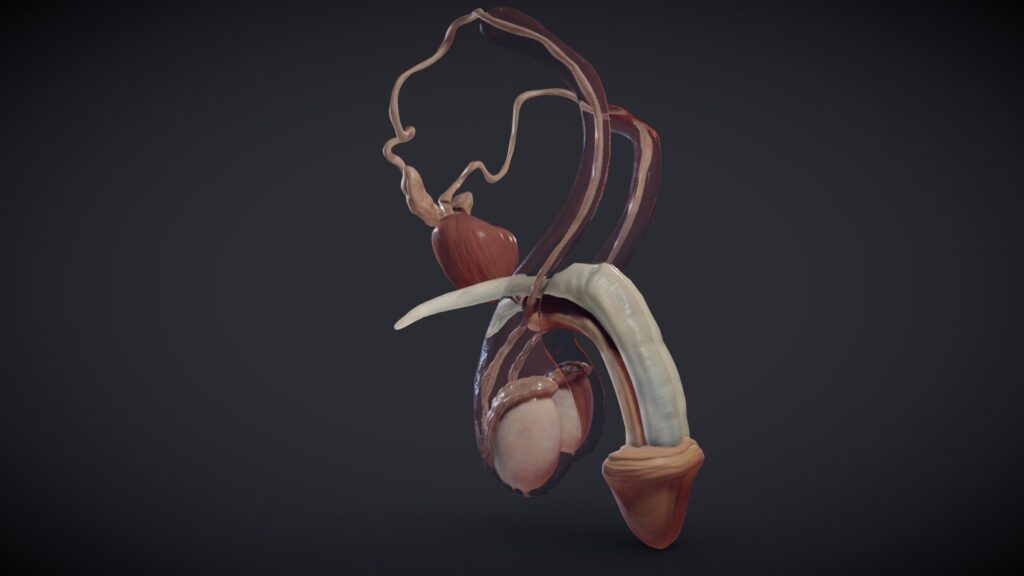
Anatomy of the Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system is comprised of both internal and external organs. Each component plays a specific and essential role in the process of reproduction.
External Organs
- Penis: The primary external organ, the penis, is responsible for both sexual intercourse and urination. It is composed of the root, body (shaft), and glans (head). The glans is covered by the foreskin, which can be removed through circumcision. The penis contains erectile tissue that becomes engorged with blood during sexual arousal, leading to an erection.
- Scrotum: The scrotum is a pouch of skin that houses the testicles. Its primary function is to regulate the temperature of the testicles, keeping them slightly cooler than the body’s core temperature. This temperature regulation is critical for sperm production.
Internal Organs
- Testes (Testicles): The testicles, also known as the testes, are the primary male reproductive organs. They are responsible for producing sperm and the male sex hormone testosterone. Each testicle is enclosed in a tough fibrous capsule called the tunica albuginea. Inside the testicles are seminiferous tubules, where sperm production (spermatogenesis) takes place.
- Epididymis: The epididymis is a coiled tube located on the back of each testicle. It serves as a storage and maturation site for sperm. As sperm travel through the epididymis, they mature and gain the ability to move.
- Vas Deferens: The vas deferens is a muscular tube that transports sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts. It passes through the spermatic cord, which also contains blood vessels and nerves.
- Seminal Vesicles: The seminal vesicles are glands that produce a fluid rich in fructose, which provides energy for the sperm. This fluid makes up a significant portion of semen.
- Prostate Gland: The prostate gland is a walnut-sized gland located below the bladder. It produces a fluid that nourishes and protects sperm. The prostate fluid is also a component of semen.
- Bulbourethral Glands (Cowper’s Glands): These small glands are located below the prostate. They secrete a clear fluid that lubricates the urethra and neutralizes any acidity.
- Urethra: The urethra is a tube that carries both urine and semen out of the body. It passes through the prostate and the penis.
Function of the Male Reproductive System
The primary function of the male reproductive system is to produce sperm and deliver it to the female reproductive system for fertilization. This complex process involves several coordinated steps.
Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis, the production of sperm, occurs in the seminiferous tubules of the testes. This process is regulated by hormones, including follicle-stimulating hormone (FSH) and luteinizing hormone (LH) from the pituitary gland, and testosterone from the testes. The entire process, from the development of sperm cells to the release of mature sperm, takes approximately 74 days.
Hormonal Regulation
The male reproductive system is heavily influenced by hormones. Testosterone, produced by the testes, is essential for the development of male secondary sexual characteristics, such as muscle mass, facial hair, and a deeper voice. It also plays a crucial role in sperm production and sexual function. The hypothalamus and pituitary gland in the brain control the production of testosterone through the release of gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH), LH, and FSH.
Ejaculation
Ejaculation is the process by which semen is expelled from the penis. During sexual arousal, the muscles in the vas deferens contract, propelling sperm from the epididymis to the ejaculatory ducts. The seminal vesicles and prostate gland secrete fluids that combine with the sperm to form semen. The bulbourethral glands also contribute lubricating fluid. The semen then passes through the urethra and is expelled from the penis during ejaculation.
Common Health Issues of the Male Reproductive System
The male reproductive system is susceptible to various health issues that can affect fertility, sexual function, and overall well-being. Regular check-ups and awareness of potential problems are crucial for maintaining optimal health.
Prostate Problems
The prostate gland is a common site of problems in men. Benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) is a non-cancerous enlargement of the prostate that can cause urinary symptoms such as frequent urination, difficulty starting urination, and a weak urine stream. Prostate cancer is another serious condition that affects the prostate gland. Regular prostate exams, including digital rectal exams and prostate-specific antigen (PSA) tests, are essential for early detection.
Testicular Problems
Testicular problems can include testicular cancer, which is most common in young men. Early detection through self-exams and regular check-ups is critical for successful treatment. Other testicular issues include testicular torsion, a medical emergency where the testicle twists, cutting off blood supply, and epididymitis, an inflammation of the epididymis, often caused by infection.
Erectile Dysfunction (ED)
Erectile dysfunction, the inability to achieve or maintain an erection sufficient for sexual intercourse, is a common problem that can affect men of all ages. Causes of ED can range from physical conditions, such as heart disease and diabetes, to psychological factors, such as stress and anxiety. Treatment options include lifestyle changes, medications, and, in some cases, surgery.
Infertility
Infertility, the inability to conceive a child after a year of unprotected intercourse, can affect both men and women. In men, infertility can be caused by a variety of factors, including low sperm count, poor sperm motility (movement), and abnormal sperm morphology (shape). Treatment options include lifestyle changes, medications, and assisted reproductive technologies (ART) such as in vitro fertilization (IVF).
Sexually Transmitted Infections (STIs)
STIs, such as chlamydia, gonorrhea, and HIV, can affect the male reproductive system and cause various health problems. Practicing safe sex, including using condoms, is essential for preventing STIs. Regular STI testing is also recommended, especially for individuals with multiple sexual partners.
Maintaining a Healthy Male Reproductive System
Several lifestyle choices can help maintain the health of the male reproductive system.
- Regular Exercise: Regular physical activity can improve overall health and may positively impact sperm quality.
- Healthy Diet: A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and lean protein can support reproductive health.
- Maintaining a Healthy Weight: Obesity can negatively affect hormone levels and sperm production.
- Avoiding Smoking and Excessive Alcohol Consumption: These habits can damage sperm and impair reproductive function.
- Stress Management: High levels of stress can affect hormone levels and sexual function.
- Regular Check-ups: Routine medical check-ups, including prostate exams and testicular self-exams, are important for early detection of potential problems.
By understanding the anatomy and function of the male reproductive system, men can take proactive steps to maintain their reproductive health and overall well-being. Awareness of potential health issues and prompt medical attention are crucial for preventing and treating problems. The male reproductive system is a complex and vital part of the human body, and its health is essential for both individual well-being and the ability to reproduce. This complete guide provides a foundation for understanding and caring for this important system.
The information provided in this guide is for general knowledge and informational purposes only, and does not constitute medical advice. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment. Maintaining a healthy male reproductive system is a crucial aspect of overall well-being, and understanding its intricacies empowers men to take control of their health. The male reproductive system’s health is impacted by various factors, and proactive measures can significantly improve outcomes.
The information above about the male reproductive system is based on current medical knowledge and understanding. The male reproductive system is a complex and dynamic entity, and ongoing research continues to refine our understanding of its function and potential health issues. Regular check-ups and open communication with healthcare providers are key to maintaining optimal health and addressing any concerns that may arise. Further research into the male reproductive system continues to provide new insights and advancements in treatment and prevention.
The male reproductive system is a fascinating and complex system. Understanding its components and functions is crucial for men’s health. By taking proactive steps and seeking medical advice when necessary, men can maintain a healthy and functional reproductive system. The health of the male reproductive system is directly linked to overall well-being. The male reproductive system requires specific care to maintain optimal health. Early detection of problems within the male reproductive system is critical for successful treatment.
The male reproductive system is integral to male health. This guide has offered a comprehensive overview of the male reproductive system, providing valuable insights into its anatomy, function, and potential health concerns. By understanding the intricacies of the male reproductive system, men can make informed decisions about their health and seek appropriate medical care when needed. The importance of the male reproductive system cannot be overstated. The functionality of the male reproductive system is essential for reproduction and overall health. The male reproductive system is a source of both physical and emotional well-being for men. The male reproductive system is a critical component of the human body.
The male reproductive system plays a vital role in both sexual function and reproduction. The male reproductive system is a complex interplay of hormones and organs. The health of the male reproductive system is a significant factor in overall health. The male reproductive system is a crucial aspect of men’s health.
Conclusion
The male reproductive system is a complex and vital system, essential for both reproduction and overall health. Through understanding its anatomy, function, and potential health issues, men can take proactive steps to maintain their reproductive well-being. Regular check-ups, a healthy lifestyle, and prompt medical attention are crucial for ensuring optimal health and addressing any concerns that may arise. The health of the male reproductive system is an integral part of a man’s overall well-being.
[See also: Prostate Cancer: Symptoms, Diagnosis, and Treatment]
[See also: Erectile Dysfunction: Causes and Treatment Options]
[See also: Understanding Male Infertility]
[See also: The Impact of Lifestyle on Sperm Quality]