Living with a Failed Cervical Fusion: Navigating Pain and Finding Relief
For individuals who undergo cervical fusion surgery, the hope is often a future free from chronic neck pain and debilitating neurological symptoms. However, in some cases, the surgery doesn’t provide the anticipated relief, leading to a failed cervical fusion. This can be a challenging and frustrating experience, leaving patients grappling with persistent pain, limited mobility, and a significant impact on their quality of life. This article delves into the complexities of living with a failed cervical fusion, offering insights into understanding the condition, managing pain, and exploring potential treatment options.
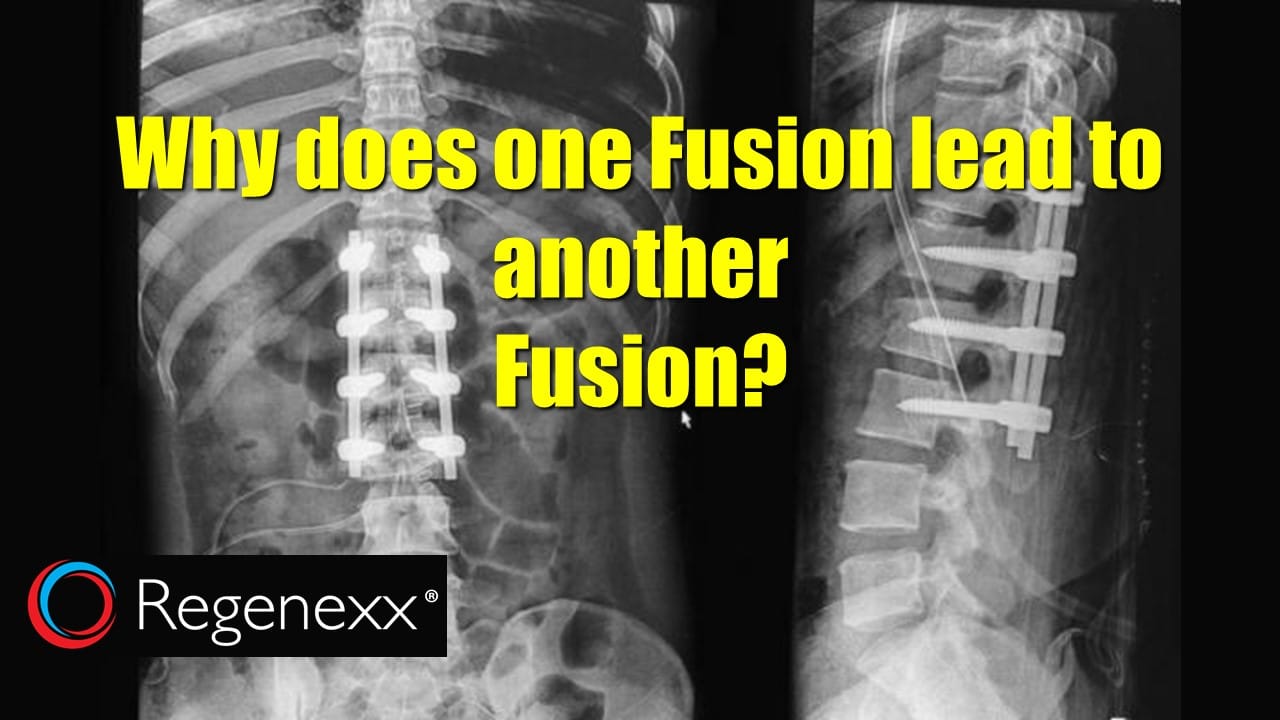
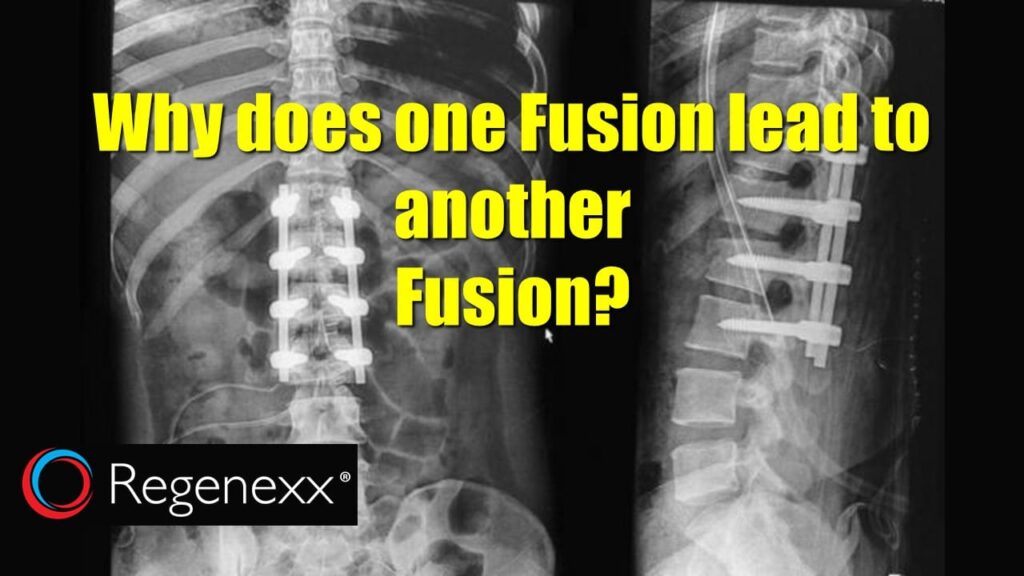
A failed cervical fusion, also known as non-union or pseudarthrosis, occurs when the bones in the neck fail to fuse properly after surgery. This can happen for various reasons, including poor bone quality, inadequate surgical technique, non-compliance with post-operative instructions, or underlying medical conditions. The consequences can be significant, with many patients experiencing persistent pain, stiffness, and neurological symptoms.
Dealing with a failed cervical fusion requires a multifaceted approach. Understanding the condition, exploring pain management strategies, and considering potential treatment options are crucial steps in navigating this complex medical challenge. This article provides a comprehensive overview of what it means to live with a failed cervical fusion, offering practical advice and information to help patients find relief and improve their overall well-being.
Understanding Failed Cervical Fusion
Cervical fusion surgery aims to stabilize the cervical spine by joining two or more vertebrae together. This is often performed to alleviate pain caused by conditions such as degenerative disc disease, spinal stenosis, or herniated discs. Successful fusion leads to a solid bony bridge between the vertebrae, eliminating motion and reducing pain. However, when the fusion fails, the bones do not heal together as intended, leading to instability and persistent symptoms.
Several factors can contribute to a failed cervical fusion. These include:
- Poor Bone Quality: Osteoporosis or other conditions that weaken the bones can hinder the fusion process.
- Smoking: Nicotine and other chemicals in tobacco can interfere with bone healing.
- Inadequate Surgical Technique: Improper placement of hardware or insufficient bone grafting can compromise the fusion.
- Non-Compliance with Post-Operative Instructions: Failing to adhere to restrictions, such as avoiding heavy lifting or twisting the neck, can disrupt the healing process.
- Underlying Medical Conditions: Diabetes, rheumatoid arthritis, and other conditions can affect bone healing.
The symptoms of a failed cervical fusion can vary depending on the severity of the non-union and the individual’s overall health. Common symptoms include:
- Persistent Neck Pain: This is often the most prominent symptom, and it can range from a dull ache to sharp, shooting pain.
- Stiffness: Limited range of motion in the neck is a common complaint.
- Headaches: Pain can radiate from the neck to the head, causing headaches.
- Radiculopathy: Nerve compression can lead to pain, numbness, or weakness in the arms or hands.
- Myelopathy: Spinal cord compression can cause more severe neurological symptoms, such as difficulty with coordination and balance.
Managing Pain Associated with a Failed Cervical Fusion
Managing pain is a critical aspect of living with a failed cervical fusion. A variety of strategies can be employed to alleviate pain and improve the patient’s quality of life. These strategies often involve a combination of approaches, tailored to the individual’s specific needs and symptoms.
Medications:
- Over-the-counter pain relievers: Such as ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin) or naproxen (Aleve) can help manage mild to moderate pain.
- Prescription pain medications: These may include stronger analgesics, such as opioids, for more severe pain. However, these medications carry the risk of side effects and addiction and should be used cautiously.
- Muscle relaxants: These medications can help reduce muscle spasms and stiffness.
- Antidepressants: Certain antidepressants, such as those in the tricyclic or SNRI classes, can be effective in managing chronic pain.
- Nerve pain medications: Medications like gabapentin or pregabalin can help reduce neuropathic pain.
Physical Therapy:
Physical therapy plays a vital role in managing pain and improving function. A physical therapist can develop a personalized exercise program that includes:
- Range-of-motion exercises: To maintain or improve neck mobility.
- Strengthening exercises: To support the neck muscles and improve stability.
- Posture correction: To address any postural imbalances that may be contributing to pain.
- Manual therapy: Such as massage or mobilization techniques, to reduce pain and stiffness.
Other Pain Management Techniques:
- Heat and cold therapy: Applying heat or cold packs can help reduce pain and inflammation.
- TENS (Transcutaneous Electrical Nerve Stimulation): This involves using a device to deliver electrical impulses to the nerves to reduce pain.
- Acupuncture: This ancient Chinese practice involves inserting thin needles into specific points on the body to stimulate the nervous system and reduce pain.
- Mind-body techniques: Such as meditation, yoga, and deep breathing exercises, can help manage pain and reduce stress.
It is essential to work closely with a healthcare provider to develop a comprehensive pain management plan that addresses the specific needs of the individual. This plan may involve a combination of medications, physical therapy, and other pain management techniques.
Exploring Potential Treatment Options for Failed Cervical Fusion
When conservative treatments fail to provide adequate relief, further interventions may be necessary to address the underlying cause of the failed cervical fusion. The treatment options will depend on the severity of the non-union, the patient’s symptoms, and their overall health. These options include:
Conservative Management:
Even in cases of failed fusion, conservative treatments may still be beneficial in managing symptoms. These can include:
- Pain medication: As described above.
- Physical therapy: To improve neck strength and mobility.
- Activity modification: Avoiding activities that aggravate pain.
- Assistive devices: Such as a cervical collar, to provide support and limit neck movement.
Surgical Interventions:
If conservative treatments are not effective, surgery may be considered. The goal of surgery is to achieve a successful fusion and alleviate pain. Surgical options may include:
- Revision surgery: This involves removing the existing hardware and bone graft and performing a new fusion. This may involve using different techniques or bone grafting materials.
- Anterior approach: The surgeon accesses the spine through the front of the neck.
- Posterior approach: The surgeon accesses the spine through the back of the neck.
- Bone grafting: Bone grafts can be harvested from the patient’s own body (autograft) or from a donor (allograft). Synthetic bone grafts are also available.
- Hardware: Screws, plates, and rods may be used to stabilize the spine during the fusion process.
The decision to undergo surgery is complex and should be made in consultation with a qualified spine surgeon. The surgeon will consider the patient’s individual circumstances, including the severity of the non-union, the patient’s symptoms, and their overall health, to determine the most appropriate treatment approach.
Living a Fulfilling Life with a Failed Cervical Fusion
Living with a failed cervical fusion can be challenging, but it does not have to prevent individuals from living fulfilling lives. By understanding the condition, managing pain effectively, and exploring available treatment options, patients can take control of their health and improve their quality of life. Here are some tips for managing the challenges of living with a failed cervical fusion:
- Seek professional help: Consult with a spine specialist to obtain an accurate diagnosis and develop a comprehensive treatment plan.
- Follow your doctor’s instructions: Adhere to all post-operative instructions and recommendations.
- Manage pain effectively: Explore various pain management strategies, including medications, physical therapy, and other techniques.
- Stay active: Engage in regular exercise and physical activity, as tolerated, to maintain strength, flexibility, and overall health.
- Prioritize your mental health: Chronic pain can take a toll on mental well-being. Seek support from a therapist or counselor to cope with stress, anxiety, and depression.
- Join a support group: Connect with others who have experienced a failed cervical fusion. Sharing experiences and providing mutual support can be invaluable.
- Advocate for yourself: Be an active participant in your healthcare. Ask questions, express your concerns, and work collaboratively with your healthcare team.
- Make lifestyle adjustments: Modify your activities and routines to accommodate your limitations. This may involve making changes to your work environment, hobbies, or daily tasks.
- Consider assistive devices: Utilize assistive devices, such as a cervical collar or ergonomic aids, to reduce strain on your neck.
- Maintain a healthy lifestyle: Eat a balanced diet, get enough sleep, and avoid smoking to promote overall health and well-being.
Living with a failed cervical fusion requires ongoing management and adaptation. It is essential to be patient with yourself, seek support from healthcare professionals and loved ones, and focus on activities that bring joy and meaning to your life. While the journey may be challenging, it is possible to find relief, improve function, and live a fulfilling life. The information provided in this article is intended for general knowledge and informational purposes only, and does not constitute medical advice. It is essential to consult with a qualified healthcare professional for any health concerns or before making any decisions related to your health or treatment.
This article provides information on living with a failed cervical fusion and how to manage the pain. The key to managing failed cervical fusion is to understand the condition, explore pain management strategies, and consider potential treatment options. If you are experiencing symptoms of a failed cervical fusion, it is important to seek medical attention and consult with a spine specialist. Managing the pain associated with a failed cervical fusion is crucial for improving quality of life. Remember, there are various treatment options available for a failed cervical fusion, and the best approach will depend on your individual needs. While living with a failed cervical fusion can be challenging, it’s possible to find relief and improve your overall well-being. Dealing with a failed cervical fusion requires a multifaceted approach. The article aims to help individuals understand the complexities of living with a failed cervical fusion and provide practical advice. Finding strategies to cope with the pain of a failed cervical fusion is key. This information can help individuals navigate the challenges of failed cervical fusion. The article aims to help those living with a failed cervical fusion navigate their experience.
[See also: Related Article Titles]