Banana Spider Egg Sac: Decoding the Mystery of Hatching
The world of arachnids, with its intricate webs and diverse species, has always captivated human curiosity. Among these fascinating creatures, the banana spider, also known as the golden silk orb-weaver (Trichonephila clavipes), stands out for its impressive size, vibrant coloration, and the complex architecture of its webs. One of the most intriguing aspects of the banana spider’s life cycle is the egg sac, a silken structure that holds the future generations. Understanding the banana spider egg sac is crucial for anyone interested in these spiders, and a key question revolves around predicting the hatching date.
This article delves into the specifics of the banana spider egg sac, exploring its structure, the factors influencing hatching, and the methods used to estimate the banana spider egg sac hatching date. We’ll navigate the complexities of their life cycle, examine the environmental influences, and discuss how to identify and study these remarkable structures. Our focus remains on providing accurate and accessible information, blending scientific rigor with engaging storytelling to unravel the mysteries surrounding the banana spider egg sac.
The Anatomy of a Banana Spider Egg Sac
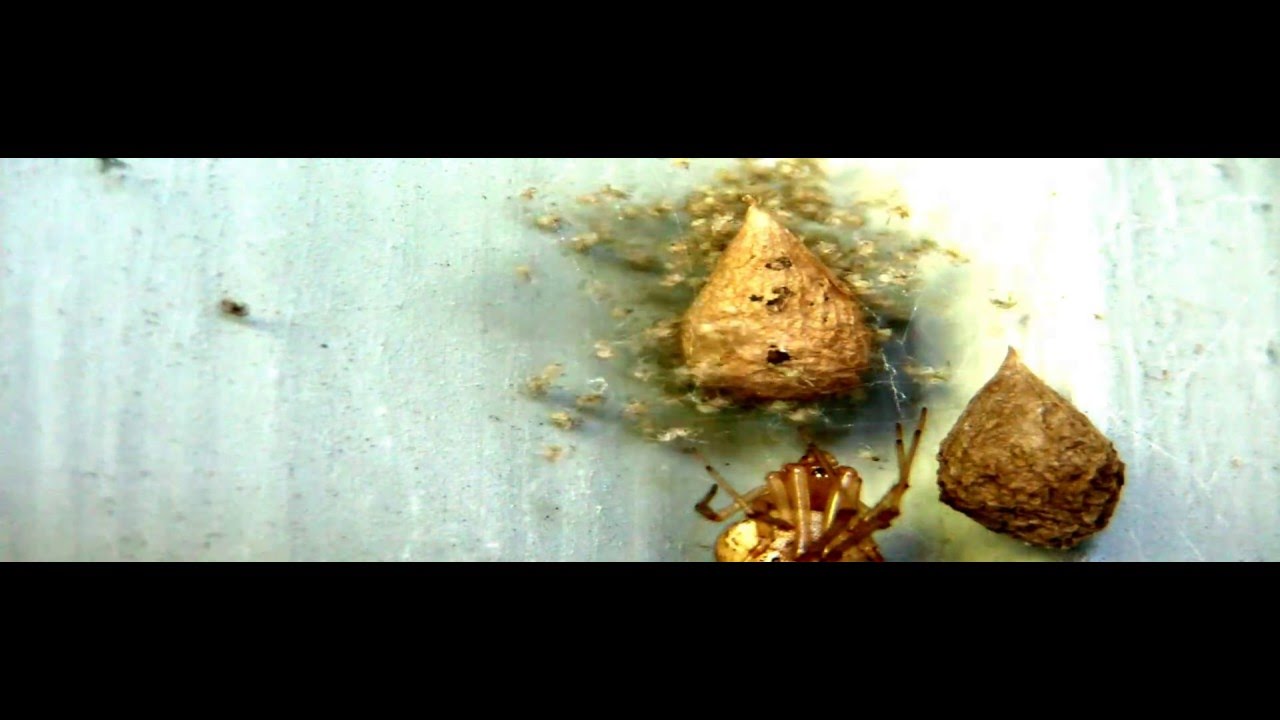
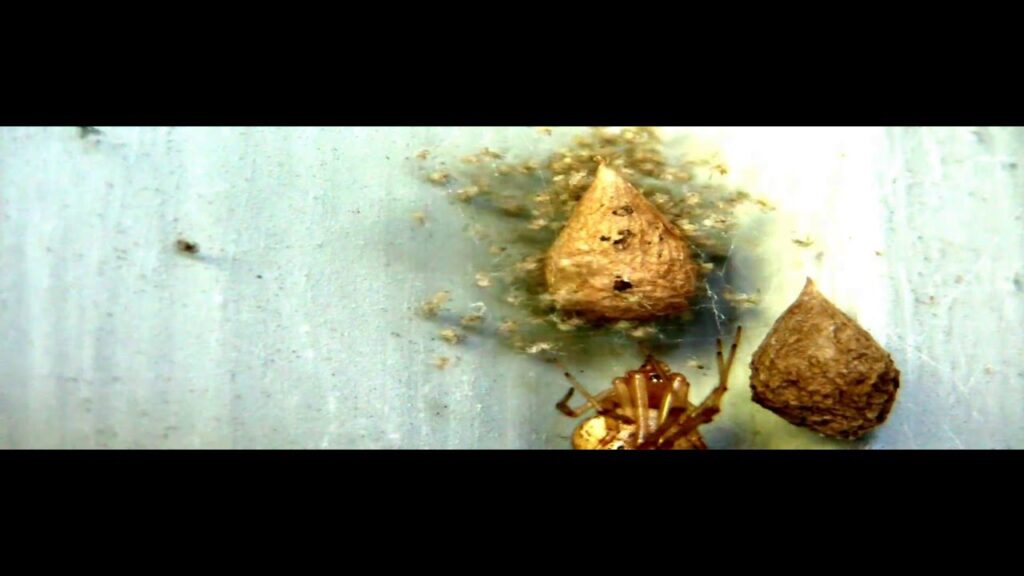
The banana spider egg sac is not merely a haphazard collection of silk; it’s a meticulously crafted structure designed to protect the developing spiderlings. The female banana spider constructs this sac with a specialized silk, often referred to as “dragline silk,” known for its strength and elasticity. The banana spider egg sac typically has a teardrop or pear shape, although variations exist based on the spider’s location, age, and environmental conditions.
Inside the banana spider egg sac, the eggs are clustered together, often numbering in the hundreds or even thousands, depending on the spider’s size and maturity. The silk of the sac provides a protective barrier against predators, harsh weather conditions, and desiccation. The thickness and composition of the silk can vary, offering different levels of protection depending on the environmental challenges faced by the spider.
The color of the banana spider egg sac can also provide clues about its age and condition. Freshly laid sacs are often a pale yellow or cream color, gradually darkening over time. The texture can range from smooth to slightly textured, depending on the silk composition and the spider’s weaving technique.
Factors Influencing Hatching: A Delicate Balance
Predicting the hatching date of a banana spider egg sac is not an exact science, as several environmental factors influence the development and emergence of the spiderlings. The primary factors include temperature, humidity, and the availability of food resources for the emerging spiderlings. Understanding these factors is crucial for estimating the hatching date.
Temperature: Temperature is perhaps the most significant factor. Warmer temperatures accelerate the development of the spiderlings inside the egg sac, while cooler temperatures slow it down. The ideal temperature range for development depends on the specific geographic location and the spider’s adaptations.
Humidity: Humidity is essential for preventing the eggs from drying out. The banana spider egg sac is designed to maintain a stable microclimate, but extreme dryness can be detrimental. High humidity generally supports the development, while excessively dry conditions can hinder it.
Light: While light is not as critical as temperature and humidity, it can still play a role. Some studies suggest that exposure to light, particularly sunlight, can influence the development of the spiderlings. However, this effect is typically secondary to the effects of temperature and humidity.
Food Availability: Although the spiderlings initially feed on the yolk sac within the egg, the availability of food sources in the surrounding environment is crucial for their survival after hatching. The presence of small insects and other prey items can influence the timing of hatching, as the spiderlings are more likely to emerge when food is readily available.
Estimating the Hatching Date: Methods and Considerations
Accurately predicting the banana spider egg sac hatching date requires careful observation and consideration of the environmental factors. Several methods can be employed, ranging from simple visual inspections to more sophisticated techniques involving temperature and humidity monitoring.
Visual Inspection: The most basic method involves regular visual inspections of the banana spider egg sac. Changes in color, texture, and size can provide clues about the stage of development. A darkening of the sac, changes in its shape, or the appearance of small movements within the sac may indicate that hatching is imminent.
Temperature Monitoring: Monitoring the temperature of the environment surrounding the banana spider egg sac is crucial. Using a thermometer to track daily temperature fluctuations can help estimate the rate of development. Consistent warm temperatures will likely accelerate the hatching process.
Humidity Monitoring: Measuring the humidity levels is also essential. A hygrometer can be used to monitor the humidity, ensuring that the environment is optimal for the spiderlings’ development. Consistent high humidity is generally favorable.
Record Keeping: Keeping detailed records of observations, temperature, and humidity readings can improve the accuracy of predictions. Noting the date the egg sac was first observed, changes in its appearance, and environmental conditions can help refine the estimate.
Online Resources and Expert Advice: Consult online resources, such as arachnid forums, scientific articles, and websites dedicated to spider identification. Seek advice from entomologists or spider experts if possible. They can provide valuable insights and guidance based on their experience and knowledge.
Challenges and Limitations in Prediction
Predicting the precise banana spider egg sac hatching date is a complex task. Several factors can introduce uncertainties and limitations. These include:
Environmental Variability: Natural environments are subject to unpredictable fluctuations in temperature, humidity, and other factors. Sudden changes in weather can significantly impact the hatching process.
Genetic Variation: Genetic differences between individual spiders can lead to variations in development rates. Some spiderlings may develop faster than others, even under identical environmental conditions.
Limited Data: The availability of data on the specific environmental conditions and the spider’s life cycle in a particular location can be limited. Without detailed information, accurate predictions are more challenging.
Human Error: The accuracy of predictions depends on the observer’s diligence and attention to detail. Errors in observation or record-keeping can lead to inaccurate estimates.
Ethical Considerations When Observing the Banana Spider Egg Sac
Observing and studying the banana spider egg sac provides an opportunity to learn about these fascinating creatures. However, ethical considerations are paramount. Responsible observation involves minimizing disturbance to the spiders and their environment. Here are some guidelines:
Avoid Disturbing the Web: Avoid touching or disturbing the spider’s web, especially if the spider is present. This can disrupt the spider’s activities and cause it stress.
Respect the Spider’s Space: Observe the spider from a distance, and avoid getting too close. This minimizes the risk of disturbing the spider or its egg sac.
Document Observations: Keep detailed records of observations, including the date, time, location, and any changes observed in the egg sac or the surrounding environment. Photographs or videos can be helpful for documenting the process.
Avoid Handling the Egg Sac: Avoid handling the banana spider egg sac, as this can damage the delicate silk structure and potentially harm the developing spiderlings. Only handle the sac if it is absolutely necessary for research purposes, and then do so with extreme care.
Respect the Spider’s Habitat: Be mindful of the spider’s habitat and avoid disturbing it. Avoid removing vegetation or other elements that provide shelter or food for the spider.
Further Research and Exploration
The study of the banana spider egg sac is an ongoing area of research. Scientists continue to explore the intricacies of the spider’s life cycle, the factors influencing development, and the impact of environmental changes. Several avenues for further research and exploration exist:
Comparative Studies: Comparing the egg sacs of different species of orb-weaver spiders can provide insights into the evolution of these structures and their adaptations to different environments.
Experimental Studies: Conducting controlled experiments to manipulate temperature, humidity, and other environmental factors can help determine their effects on the hatching process.
Genetic Analysis: Analyzing the genetics of the spiderlings can provide insights into the factors influencing development rates and other aspects of their biology.
Ecological Studies: Studying the ecological role of the banana spider and its egg sac can help understand their impact on the ecosystem.
Conclusion: Unraveling the Secrets of the Banana Spider Egg Sac
The banana spider egg sac is a testament to the intricate design of nature. Understanding its structure, the factors influencing hatching, and the methods for estimating the hatching date is essential for anyone interested in the biology and behavior of these fascinating spiders. By carefully observing these structures, monitoring environmental conditions, and respecting the spiders’ habitat, we can gain a deeper appreciation for the wonders of the natural world. The ability to predict the banana spider egg sac hatching date is a combination of observation, scientific understanding, and a bit of patience. It is a rewarding pursuit for anyone interested in the fascinating world of arachnids.
[See also: Spider Web Construction: A Marvel of Engineering, The Venom of the Banana Spider: What You Need to Know, How to Identify Different Spider Species]