Decoding the PCB Input Jack Wiring: A Guide for Audiophiles Seeking Pristine Sound
The pursuit of audio perfection is a journey for the dedicated audiophile. Every component, from the amplifier to the speakers, plays a crucial role in shaping the final sound. Often overlooked, the humble input jack, particularly its Printed Circuit Board (PCB) wiring, can significantly impact the audio signal’s fidelity. This article delves into the intricacies of PCB input jack wiring for audiophiles, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding, optimizing, and troubleshooting this critical aspect of high-fidelity audio systems.
Understanding the Significance of Input Jacks
The input jack is the gateway through which audio signals enter your system. Whether it’s from a turntable, CD player, or digital audio player, the quality of this initial connection is paramount. Poorly wired or designed input jacks can introduce noise, distortion, and signal loss, degrading the listening experience. For audiophiles, who demand the purest possible sound reproduction, understanding the nuances of PCB input jack wiring is non-negotiable.
The Anatomy of a PCB Input Jack
A PCB input jack typically consists of several key components:
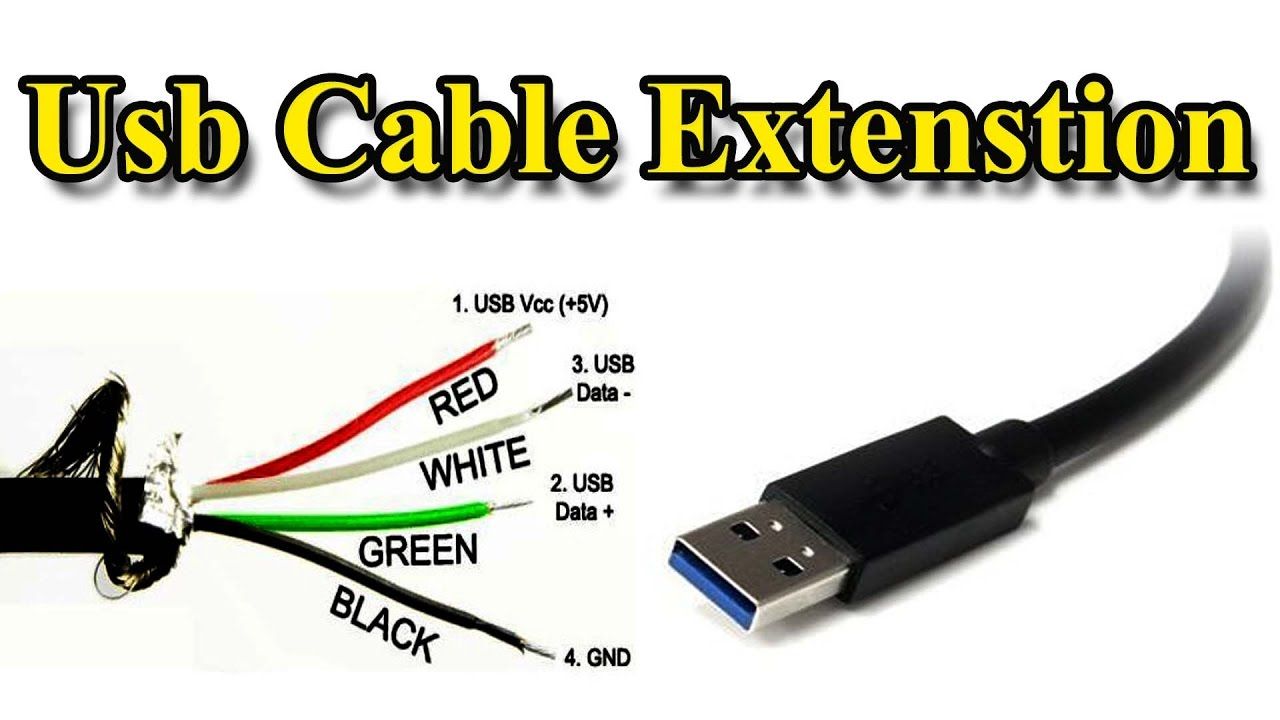
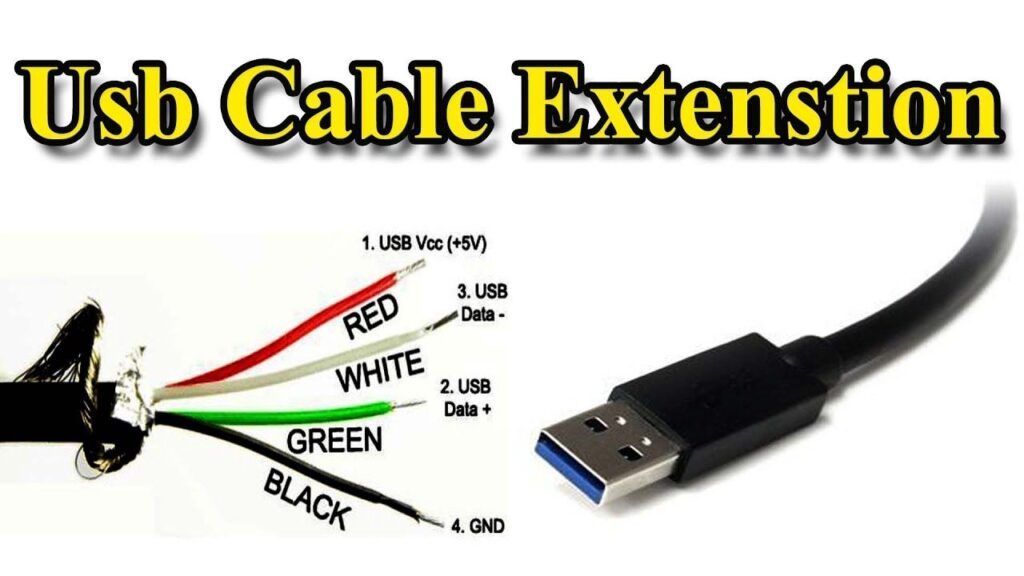
- The Jack Itself: This is the physical connector, often a 1/4-inch (6.35mm) or RCA type, that receives the audio cable.
- Solder Pads: These are the metal pads on the PCB where the jack’s terminals are soldered.
- Traces: These are the conductive pathways on the PCB that connect the solder pads to other components in the audio circuit.
- Ground Plane: A large area of copper on the PCB, often connected to the ground, to minimize noise and interference.
The quality of these components, and the precision with which they are connected, directly affects the audio signal’s integrity. Understanding this anatomy is the first step in mastering PCB input jack wiring.
Common Issues with PCB Input Jack Wiring
Several issues can plague PCB input jack wiring, leading to degraded audio performance. These include:
- Poor Solder Joints: Cold solder joints or insufficient solder can create intermittent connections, causing crackling, signal loss, or complete failure.
- Improper Grounding: Inadequate grounding can introduce hum, buzz, and other noise into the audio signal.
- Trace Length and Layout: Long or poorly routed traces can act as antennas, picking up unwanted radio frequency interference (RFI) or electromagnetic interference (EMI).
- Component Quality: Using low-quality jacks or PCB materials can contribute to signal degradation.
Identifying these issues is crucial for troubleshooting and improving the audio quality of your system. Regular inspection and meticulous attention to detail are key.
Optimizing PCB Input Jack Wiring for Audiophile Performance
Several techniques can be employed to optimize PCB input jack wiring for superior audio performance:
Choosing High-Quality Components
Investing in high-quality jacks, connectors, and PCB materials is the foundation of a great-sounding system. Look for jacks with gold-plated contacts, which resist corrosion and provide a more reliable connection. Similarly, PCBs made from high-quality materials, such as FR4, offer better electrical properties and reduced signal loss.
Meticulous Soldering Techniques
Proper soldering is critical. Use a temperature-controlled soldering iron and high-quality solder. Ensure that the solder joints are clean, shiny, and free of cold joints. Avoid excessive heat, which can damage the jack or PCB. Practice makes perfect; if you’re new to soldering, practice on scrap PCBs before working on your valuable audio equipment.
Optimizing Trace Layout
Careful trace layout is essential for minimizing noise and interference. Keep traces short and direct, especially for sensitive audio signals. Route traces away from noisy components, such as power supplies and digital circuits. Consider using a ground plane to provide a low-impedance path for ground currents and shield the audio signals from interference. This is particularly important when considering PCB input jack wiring.
Effective Grounding Strategies
Proper grounding is paramount for minimizing noise. Use a star grounding configuration, where all ground connections meet at a single point. This minimizes ground loops, which can introduce hum. Ensure that the ground plane is adequately connected to the ground terminals of the input jack and other components. For optimal results with PCB input jack wiring, consider using separate ground planes for analog and digital circuits to further reduce interference.
Shielding and Isolation
Shielding can further reduce interference. Consider using shielded cables and enclosures to protect the audio signals from external noise sources. Isolate the input jack from the chassis to prevent ground loops. These measures can significantly improve the signal-to-noise ratio and the overall audio quality. This is a key consideration when working with PCB input jack wiring.
Tools and Materials for PCB Input Jack Wiring
To successfully work with PCB input jack wiring, you’ll need the following tools and materials:
- Soldering Iron: A temperature-controlled soldering iron is highly recommended.
- Solder: Use high-quality, lead-free solder.
- Solder Wick or Desoldering Pump: For removing solder.
- Multimeter: For testing connections and troubleshooting.
- Wire Strippers and Cutters: For preparing wires.
- Input Jacks: High-quality jacks appropriate for your application.
- PCB Cleaner: For cleaning the PCB before soldering.
- Magnifying Glass: To inspect solder joints.
- Anti-Static Wrist Strap: To protect sensitive components from electrostatic discharge.
Troubleshooting Common Problems
Even with careful planning and execution, problems can arise. Here’s how to troubleshoot common issues:
- No Sound: Check the connections at both ends of the cable. Use a multimeter to test for continuity. Inspect the solder joints for any breaks or cold joints.
- Hum or Buzz: Verify that all ground connections are secure and properly connected. Check for ground loops. Try using shielded cables and isolating the input jack.
- Crackling or Intermittent Sound: Inspect the solder joints for cold joints or loose connections. Wiggle the cable and jack to see if the problem is intermittent.
- Distortion: Check the signal level and ensure that it is not overdriving the input stage. Inspect the traces for any damage or shorts.
Systematic troubleshooting is crucial. Isolate the problem by testing each component and connection. Consulting schematics and service manuals is often helpful.
The Audiophile’s Final Touch: Fine-Tuning and Listening Tests
Once the PCB input jack wiring is complete and tested, the final step is fine-tuning and listening tests. Connect your audio source and speakers and listen critically. Pay attention to the soundstage, imaging, and overall clarity. Make adjustments as needed. This is where you can truly appreciate the impact of optimized PCB input jack wiring.
Beyond the Basics: Advanced Techniques
For the advanced audiophile, further refinements are possible:
- Upgrading PCB Materials: Consider using high-performance PCBs with better dielectric properties and lower signal loss.
- Implementing Balanced Connections: Balanced connections offer superior noise rejection and are often preferred in high-end audio systems.
- Cryogenic Treatment: Some audiophiles believe that cryogenic treatment of components, including input jacks, can improve performance.
Conclusion: The Pursuit of Audio Excellence
Optimizing PCB input jack wiring is a crucial step in achieving audio excellence. By understanding the principles of good design, using high-quality components, and employing meticulous soldering techniques, audiophiles can significantly improve the performance of their audio systems. The journey to audio perfection is a continuous one, and mastering the intricacies of PCB input jack wiring is a rewarding step along the way.
By carefully considering the layout and quality of your PCB input jack wiring, you can unlock the full potential of your audio equipment and enjoy a truly immersive listening experience. This guide serves as a starting point; further research and experimentation are encouraged.
Remember that the quality of your PCB input jack wiring is a reflection of your dedication to the art of sound reproduction. Take the time to do it right, and the rewards will be clear. This is a central tenet of the audiophile philosophy, and the benefits of optimized PCB input jack wiring are undeniable.
In conclusion, the seemingly small details of PCB input jack wiring can have a significant impact on your listening pleasure. Embrace the challenge and elevate your audio experience.
[See also: Related Article Titles]