E-Brake Adjustment: Ensuring Safety and Performance Across Vehicle Types
The emergency brake, also known as the parking brake or e-brake, is a critical safety feature often overlooked until it’s needed. While its primary function is to hold a parked vehicle stationary, it also serves as a backup braking system in emergencies. Understanding the intricacies of e-brake adjustment and knowing how it applies to various car models is paramount for vehicle owners. This article provides a comprehensive overview of e-brake adjustment, covering its importance, the methods involved, and considerations for different vehicle types.
The Significance of a Properly Functioning E-Brake
A well-maintained e-brake is more than just a convenience; it’s a safety necessity. Its primary role is to prevent a parked vehicle from rolling, especially on inclines. This is crucial for preventing accidents and potential damage. Beyond this, the e-brake serves as a backup braking system. In the event of primary brake failure, the e-brake can be used to gradually bring the vehicle to a stop. This function is vital for driver and passenger safety. Regular inspection and proper e-brake adjustment are essential to ensure its reliability.
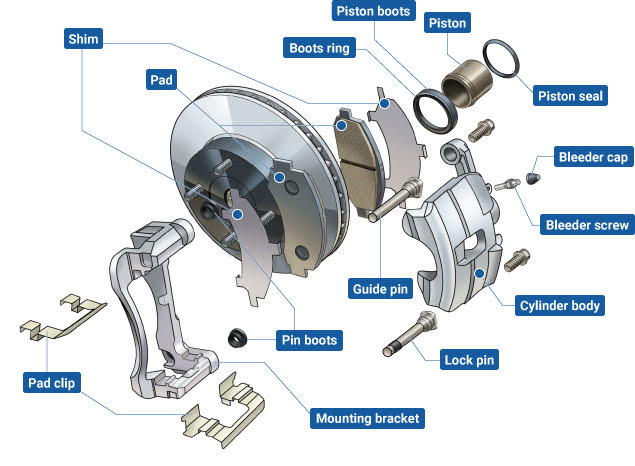
Understanding the E-Brake Mechanism
The mechanism of the e-brake varies slightly between car models, but the fundamental principles remain consistent. Most modern vehicles use a cable-operated system, where pulling the lever or pressing a foot pedal engages a cable that pulls on the rear brake calipers or drum brakes. Some newer vehicles are equipped with electronic parking brakes (EPB), which use an electric motor to actuate the brakes. Regardless of the system, the core function is to apply pressure to the rear brakes, preventing wheel rotation.
Common Symptoms Indicating the Need for E-Brake Adjustment
Several telltale signs can indicate that your e-brake requires adjustment. These include:
- Reduced Holding Power: The vehicle rolls when parked on a slight incline.
- Excessive Lever Travel: The handbrake lever needs to be pulled up or the foot pedal pressed down further than usual to engage the brake.
- Dragging Brakes: The rear brakes may feel hot, or the vehicle may feel sluggish even when the e-brake is disengaged.
- Unusual Noises: Squealing or grinding noises may be heard from the rear brakes.
- Failure to Engage: The e-brake fails to hold the vehicle, even on level ground.
If you experience any of these symptoms, it’s crucial to address them promptly. Ignoring these warning signs can compromise your vehicle’s safety and lead to more significant and costly repairs.
The Process of E-Brake Adjustment: A Step-by-Step Guide
The e-brake adjustment procedure varies depending on the vehicle’s make and model. However, the general steps typically involve the following:
- Preparation: Park the vehicle on a level surface, engage the e-brake, and chock the front wheels for added safety. Gather the necessary tools, including a jack, jack stands, wrenches, and possibly a screwdriver.
- Locating the Adjustment Mechanism: The adjustment mechanism is usually located under the center console or near the rear wheels. Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual or a repair manual to find the exact location for your specific model.
- Adjusting the Cables: For cable-operated systems, the adjustment typically involves tightening the cable tension at the adjustment nut. This nut is often located near the e-brake lever or under the vehicle. Tighten the nut gradually, checking the e-brake function after each adjustment.
- Adjusting the Rear Brakes (if applicable): Some vehicles require adjusting the rear brake shoes or pads in addition to the cable adjustment. This may involve accessing the rear brake drums or calipers and adjusting the brake shoes or pads using a screwdriver or a specific tool.
- Testing and Final Adjustments: After making the adjustments, test the e-brake by engaging it and trying to move the vehicle. The e-brake should hold the vehicle firmly. Make any final adjustments as needed to achieve the desired holding power.
If you’re not comfortable performing the e-brake adjustment yourself, it’s best to take your vehicle to a qualified mechanic. Improper adjustment can compromise the e-brake‘s effectiveness and potentially lead to safety issues.
E-Brake Adjustment Across Different Car Models
The methods and considerations for e-brake adjustment can vary significantly depending on the vehicle’s make and model. Here’s a brief overview:
Cable-Operated Systems
These are the most common type of e-brake systems. The adjustment typically involves tightening the cable at the adjustment nut. Some vehicles may also require adjusting the rear brake shoes or pads.
Electronic Parking Brake (EPB) Systems
EPB systems are becoming increasingly common in modern vehicles. These systems use an electric motor to actuate the rear brakes. E-brake adjustment for EPB systems typically involves using a diagnostic tool to put the system into service mode before adjusting the brakes. This allows the brake calipers to be retracted for adjustment. After the adjustment, the system must be put back into normal operating mode.
Vehicles with Drum Brakes
Vehicles with drum brakes may require adjusting the brake shoes in addition to the cable adjustment. This typically involves removing the brake drum and adjusting the star wheel adjuster to move the brake shoes closer to the drum.
Vehicles with Disc Brakes
Vehicles with disc brakes typically have a cable that pulls on the rear brake calipers. The adjustment usually involves tightening the cable at the adjustment nut. Some vehicles may also require adjusting the rear brake pads.
DIY vs. Professional E-Brake Adjustment
While some car owners are comfortable performing basic maintenance tasks, e-brake adjustment can be a more complex procedure, especially for those unfamiliar with automotive mechanics. Here’s a comparison to help you decide whether to tackle the job yourself or seek professional assistance:
DIY E-Brake Adjustment
Pros:
- Cost Savings: You can save money on labor costs.
- Learning Opportunity: You can learn more about your vehicle’s mechanics.
Cons:
- Requires Knowledge and Tools: You need to have the necessary knowledge, skills, and tools.
- Potential for Mistakes: Incorrect adjustments can compromise safety.
- Time-Consuming: The process can take longer than expected.
Professional E-Brake Adjustment
Pros:
- Expertise: Mechanics have the knowledge and experience to perform the adjustment correctly.
- Efficiency: The job is usually completed quickly and efficiently.
- Warranty: Professional work typically comes with a warranty.
Cons:
- Higher Cost: You’ll have to pay for labor costs.
- Inconvenience: You’ll need to take your vehicle to a mechanic.
Ultimately, the decision depends on your level of mechanical aptitude, the complexity of your vehicle’s e-brake system, and your budget. If you’re unsure about any aspect of the adjustment process, it’s always best to consult a qualified mechanic.
Maintaining Your E-Brake for Optimal Performance
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring your e-brake remains in good working order. Here are some tips:
- Regular Inspections: Have your e-brake inspected during routine vehicle maintenance.
- Use It Regularly: Engage the e-brake periodically to prevent the cables from seizing.
- Address Issues Promptly: Don’t ignore any warning signs, such as reduced holding power or excessive lever travel.
- Follow Manufacturer’s Recommendations: Consult your vehicle’s owner’s manual for specific maintenance recommendations.
By following these tips, you can help ensure that your e-brake is always ready to perform its critical safety function.
Conclusion: Prioritizing E-Brake Safety and Function
E-brake adjustment is a crucial aspect of vehicle maintenance that should not be overlooked. Whether you own a classic car with a cable-operated system or a modern vehicle with an EPB, understanding the e-brake mechanism and the adjustment process is essential for ensuring safety and performance. Regular inspections, prompt attention to any warning signs, and proper maintenance will keep your e-brake functioning reliably, providing you with peace of mind on the road.
[See also: Brake System Maintenance Tips]
[See also: Electronic Parking Brake Troubleshooting]
[See also: How to Diagnose Brake Problems]

